Achieving precision in drone imaging and mapping is essential across various industries, from agriculture to construction. Ground Sample Distance (GSD) plays a critical role in determining image resolution, as it measures the distance between pixel centers on the ground. By optimizing flight height, you can control GSD to capture finer details or cover larger areas, depending on your needs.
This guide will explore the relationship between flight height and GSD, provide tips for determining the optimal flight height, and discuss practical applications to enhance your drone operations. Whether you’re a seasoned drone operator or a newcomer, understanding how to leverage GSD can elevate your aerial imagery and data collection to new heights of accuracy and efficiency.

The Relationship Between Flight Height and GSD
Understanding the relationship between flight height and Ground Sample Distance (GSD) is crucial for optimizing your drone’s performance. This section explores how changes in flight altitude directly impact GSD, ultimately affecting the quality and precision of your drone imagery.
Direct Correlation
Ground Sample Distance (GSD) is inversely related to the flight height of your drone. This means that as the flight height increases, the GSD also increases, resulting in lower image resolution. Conversely, decreasing the flight height reduces the GSD, leading to higher-resolution images.
Impact on Image Quality
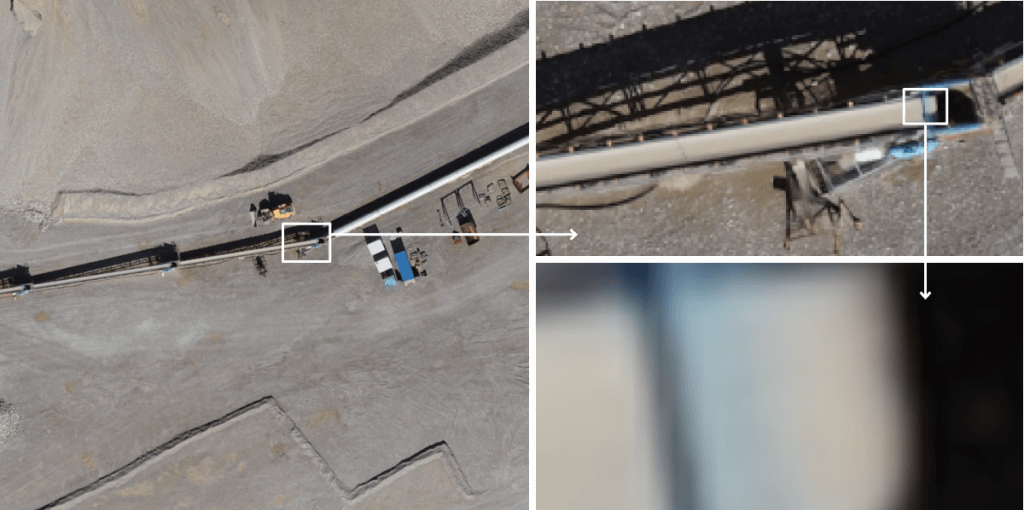
Adjusting flight height to optimize GSD significantly influences the quality of the captured images. Higher flight heights result in larger GSD values, meaning each pixel represents a larger ground area. This reduces the image’s detail and sharpness, making it less suitable for tasks requiring high precision. On the other hand, flying at lower altitudes decreases the GSD, capturing finer details and producing clearer, more detailed images. However, flying too low can limit the coverage area and increase the risk of obstacles.
By understanding and leveraging this relationship, drone operators can make informed decisions about flight planning to ensure that their imagery meets the required standards for precision and detail.
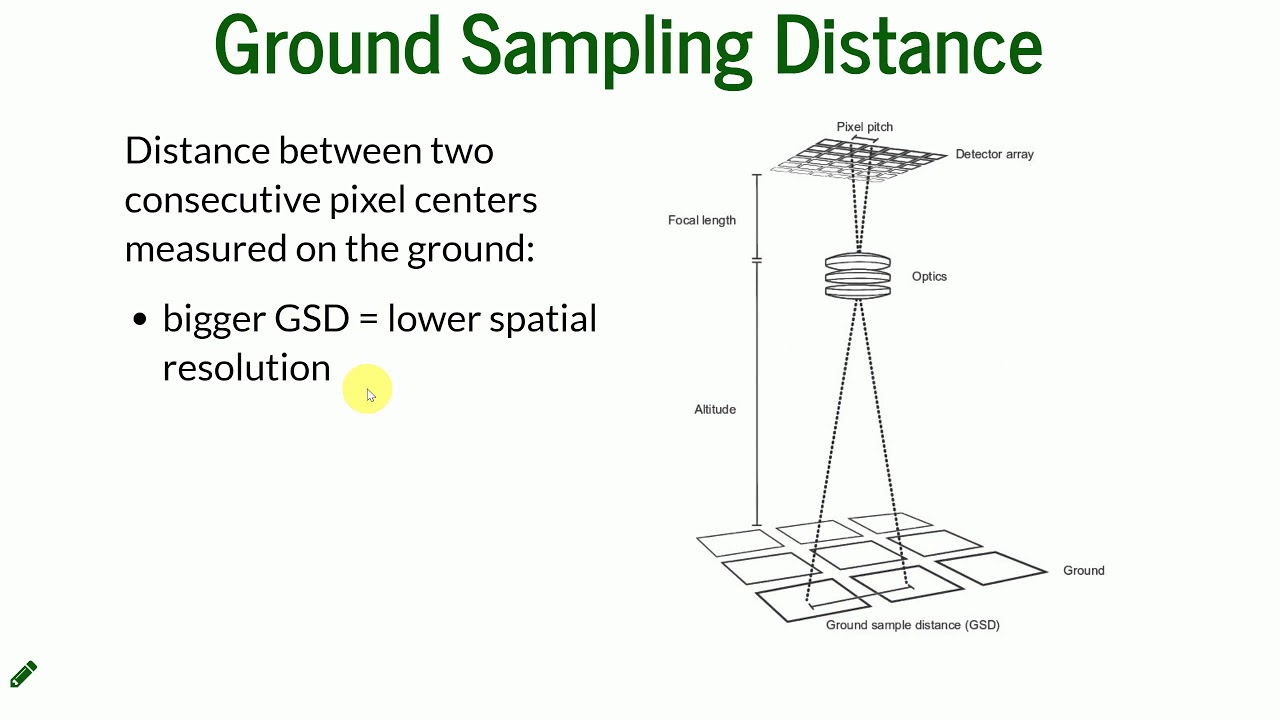
Determining Optimal Flight Height
Finding the optimal flight height for your drone operations is essential for achieving the desired Ground Sample Distance (GSD) and image quality. This section provides practical guidance on how to determine the best flight height for various applications.
Mission Objectives
Define the mission objectives to determine the required GSD. Different tasks require different levels of detail:
- Agricultural Monitoring: High-resolution images to detect small changes in crop health.
- Construction Site Surveys: Detailed imagery for accurate measurements and progress tracking.
- Environmental Monitoring: Balance between coverage area and image detail for effective monitoring of large areas.

Tools and Software
Use tools and software to calculate and optimize flight height for your desired GSD:
- Drone Flight Planning Software: Applications like DroneDeploy, Pix4D, and DJI Ground Station Pro can input your camera specifications and desired GSD to calculate the optimal flight height.
- GSD Calculators: Online calculators allow manual determination of required flight height by entering camera details and desired GSD.
- Mission Planning Apps: Mobile apps for drone pilots include features to plan missions based on GSD requirements.
Best Practices
Follow these best practices when setting your drone’s flight height:
- Consider the Terrain: Adjust flight height to avoid obstacles and ensure consistent coverage.
- Regulations and Safety: Adhere to local regulations regarding maximum flight heights and ensure safe operations.
- Weather Conditions: Choose a flight height that minimizes the impact of wind, temperature, and lighting on drone stability and image quality.
- Test Flights: Conduct test flights at different altitudes to evaluate image quality and GSD, fine-tuning the optimal flight height for your mission.
By following these guidelines and utilizing the right tools, you can determine the optimal flight height for your drone operations, ensuring precision and detail in your images and data.

Practical Applications
Optimizing flight height using Ground Sample Distance (GSD) has numerous practical applications across various industries. This section highlights key use cases where fine-tuning GSD significantly enhances outcomes.
Agriculture
In agriculture, high-resolution imagery is essential for detecting crop health issues, assessing plant growth, and managing resources. Optimizing flight height to achieve a lower GSD allows farmers to capture detailed images, revealing subtle changes in vegetation and enabling precise interventions for improved crop yields.
Construction
Construction site surveys require detailed and accurate imagery for precise measurements, progress tracking, and quality assessments. By adjusting flight height to achieve an appropriate GSD, construction managers can create detailed 3D models, monitor progress, and identify potential issues early, resulting in better project management and reduced costs.
Environmental Monitoring
For environmental monitoring, achieving a balance between coverage area and image detail is crucial. Optimizing flight height ensures that drones can cover large areas while still capturing sufficient detail to monitor changes in landscapes, wildlife habitats, and natural resources effectively.
Infrastructure Inspection
Drones used for inspecting bridges, power lines, and other infrastructure need high-resolution images to detect minor defects. Optimizing flight height ensures the GSD is small enough to capture fine details necessary for thorough inspections.

Disaster Response
After natural disasters, drones provide rapid assessment of affected areas. Balancing coverage and detail by optimizing flight height helps identify damage and prioritize response efforts, facilitating effective disaster management.
By understanding the specific requirements of different applications and optimizing flight height accordingly, drone operators can significantly enhance the quality and utility of their aerial imagery across various real-world scenarios.
Challenges and Considerations
Optimizing drone flight height for precise Ground Sample Distance (GSD) involves navigating several challenges. Weather conditions like wind and rain can affect stability and image quality, so plan flights during calm weather. Varying terrain and obstacles require careful path planning to avoid collisions. Adhering to local regulations ensures safe and legal operations. Technical limitations, such as camera resolution and battery life, must be considered to meet GSD requirements. Efficient data processing and storage solutions are necessary for managing high-resolution images. Additionally, optimizing flight height can increase operational costs, so budget accordingly to maintain quality without compromising on expenses.
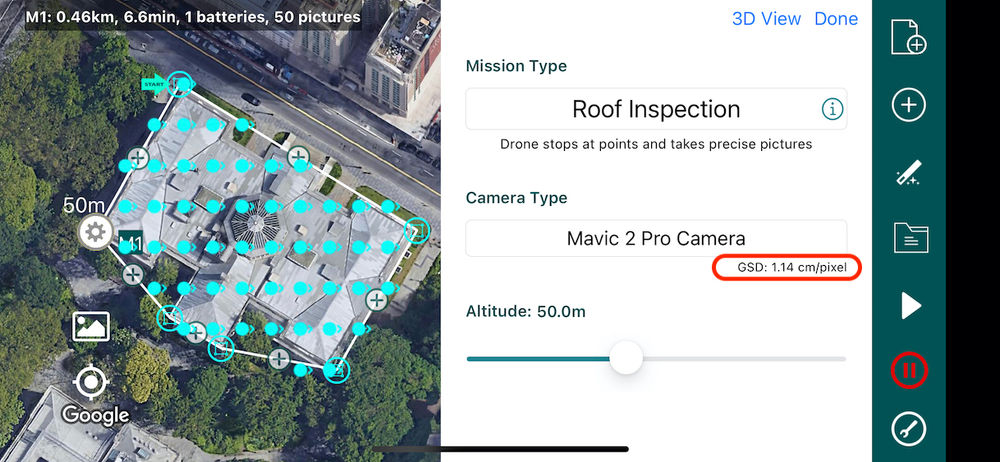
Final Thoughts: Precision in Drone Imagery through GSD Optimization
Optimizing drone flight height to achieve the desired Ground Sample Distance (GSD) is crucial for obtaining high-quality, precise imagery. By understanding the relationship between flight height and GSD, drone operators can make informed decisions to enhance their aerial data collection.
Key considerations include clearly defining mission objectives, utilizing the right tools and software for flight planning, and following best practices for different applications such as agriculture, construction, and environmental monitoring. Additionally, addressing challenges related to environmental factors, terrain, regulations, technical limitations, data processing, and cost is essential for successful operations.
By carefully planning and optimizing flight height, drone operators can ensure their missions are both efficient and effective, capturing the detailed imagery necessary for informed decision-making and project success.



